- By Marketing
- In Mold Removal
The Flu Season
While seasonal influenza (flu) viruses can be detected year-round in the United States, flu viruses are most common during the fall and winter. The exact timing and duration of flu seasons can vary, but influenza activity often begins to increase in October. Most of the time flu activity peaks between December and February, although activity can last as late as May.
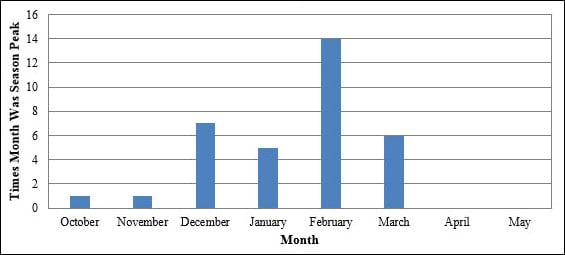
The figure below shows peak flu activity for the United States by month for the 1982-1983 through 2015-2016 flu seasons. The “peak month of flu activity” is the month with the highest percentage of respiratory specimens testing positive for influenza virus infection during that influenza season. During this 34-year period, flu activity most often peaked in February (14 seasons), followed by December (7 seasons), March (6 seasons), and January (5 seasons).
Peak Month of Flu Activity
1982-1983 through 2015-2016
Monitoring Flu Activity
CDC collects, compiles and analyzes information on influenza activity year round in the United States and produces FluView, a weekly influenza surveillance report, and FluView Interactive, which allows for more in-depth exploration of influenza surveillance data. The U.S. influenza surveillance system is a collaborative effort between CDC and its many partners in state and local health departments, public health and clinical laboratories, vital statistics offices, health care providers, and clinics and emergency departments. Information in five categories is collected from eight different data sources that allow CDC to:
- Find out when and where influenza activity is occurring
- Track influenza-related illness
- Determine what influenza viruses are circulating
- Detect changes in influenza viruses
- Measure the impact influenza is having on hospitalizations and deaths in the United States
For more information about flu surveillance or to access these reports, visit Flu Activity & Surveillance.
https://www.cdc.gov/flu/about/season/flu-season.htm
